Health
Health Benefits of Parmesan Cheese: A Deep Dive into Nutritional Advantages
Published
1 year agoon
By
Admin
Parmesan cheese offers numerous health benefits, including high levels of protein, calcium, and probiotics, making it a healthy addition to your diet when consumed in moderation.
Understanding Parmesan Cheese’s Nutritional Profile
Parmesan cheese, known for its distinctive sharp flavor and granular texture, is much more than a delicious topping for pasta.
This Italian cheese, particularly when aged, is a nutritional powerhouse rich in essential nutrients like protein, calcium, vitamins, and probiotics.
When consumed in moderation, Parmesan can offer a wide array of health benefits, from supporting bone health to improving digestion.
In this article, we’ll explore the health advantages of Parmesan cheese, breaking down why this aged dairy product is worth including in a balanced diet.
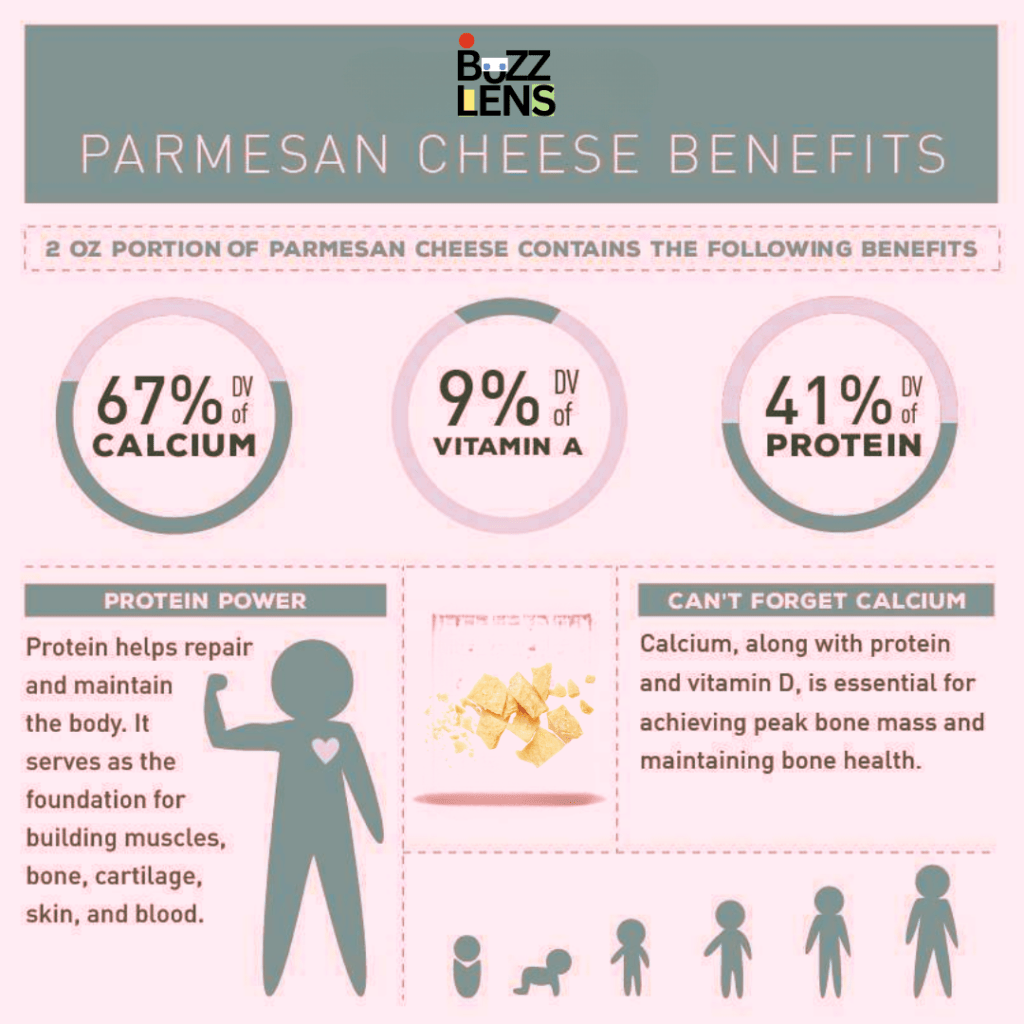
1. Rich in Protein: Essential for Body Function
Research-Based Insight: Parmesan cheese is an excellent source of high-quality protein, with 10 grams per ounce, making it a great addition for those looking to increase their protein intake without consuming too many calories.
According to a study published in the Journal of Dairy Science, aged cheeses like Parmesan provide complete proteins, containing all the essential amino acids necessary for muscle repair, growth, and immune system function.
Protein plays a critical role in building muscle, repairing tissues, and maintaining overall bodily functions. For active individuals, athletes, or those recovering from injury, incorporating Parmesan cheese into meals can help meet daily protein requirements.
Additionally, its rich flavor allows for small portions to have a big impact, making it an efficient protein source.
2. High in Calcium: Bone Health and Beyond
Research-Based Insight: Parmesan cheese is one of the richest dietary sources of calcium, offering about 331 mg of calcium per ounce, which is approximately 33% of the recommended daily intake for adults.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), calcium is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth and preventing conditions like osteoporosis.
Aged cheeses like Parmesan also have a higher bioavailability of calcium, making it easier for your body to absorb.
Calcium not only strengthens bones but also plays a role in nerve transmission, muscle function, and blood clotting.
A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that individuals who regularly consume calcium-rich foods like Parmesan are at a lower risk for bone fractures and osteoporosis, particularly in postmenopausal women and elderly adults.
Also Read: Chive: The Health-Packed Herb You Should Add to Your Diet Today
3. Probiotics and Gut Health: Aged Cheese for Digestive Support
Research-Based Insight: Parmesan cheese, being an aged cheese, contains beneficial probiotics, which promote gut health by helping to maintain a balance of good bacteria in the digestive tract.

Probiotics are essential for digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function. A study published in the British Journal of Nutrition demonstrated that probiotic-rich foods like Parmesan can reduce inflammation, improve digestion, and support a healthy microbiome.
Additionally, probiotics in Parmesan support the immune system by encouraging the growth of healthy gut bacteria, which play a crucial role in fighting off infections and diseases.
Regular consumption of aged cheeses like Parmesan can contribute to a healthier digestive system, reduce bloating, and support overall gut health.
4. Low in Lactose: Easier on Sensitive Stomachs
Research-Based Insight: Parmesan cheese is one of the few dairy products that are naturally low in lactose due to its long aging process, which breaks down most of the lactose found in milk.
A report from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) states that many people who are lactose intolerant can safely consume aged cheeses like Parmesan without experiencing discomfort.
This makes Parmesan a great alternative for individuals with lactose sensitivity.
The fermentation process that Parmesan undergoes reduces its lactose content to nearly undetectable levels, allowing it to retain its nutritional value while being easier to digest.
Also Read: Health Benefits of Strawberries: A Nutrient-Packed Superfruit
5. Rich in Essential Vitamins and Minerals
Research-Based Insight: Parmesan cheese is loaded with essential vitamins and minerals, including Vitamin A, Vitamin B12, and Riboflavin (B2).
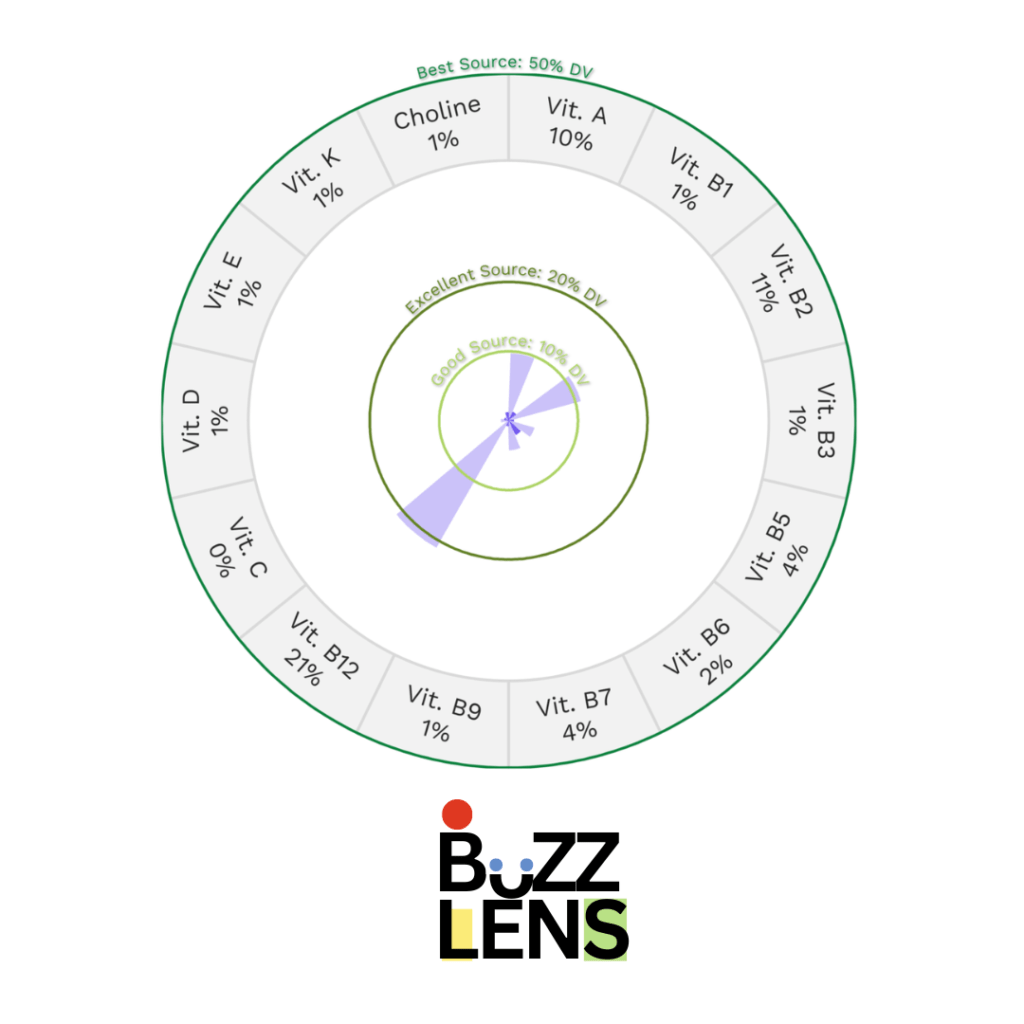
Each of these vitamins plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health:
- Vitamin A supports vision, skin health, and immune function.
- Vitamin B12 is essential for red blood cell formation, DNA synthesis, and neurological function.
- Riboflavin (B2) aids in energy production and cellular function.
A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition emphasizes the importance of incorporating these vitamins into the diet, and Parmesan cheese is an excellent source of all three.
Its nutrient density makes it an important addition for anyone looking to boost their intake of these vital compounds.
6. Low-Carb and Keto-Friendly
Research-Based Insight: Parmesan cheese contains less than 1 gram of carbohydrates per ounce, making it a perfect addition to low-carb or ketogenic diets.
These diets rely on high-fat, low-carb foods to maintain a state of ketosis, where the body burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.

According to a study published in the Journal of Nutrition, consuming high-fat, low-carb foods like Parmesan can support ketosis and help individuals maintain stable energy levels and manage weight.
Whether grated over vegetables or used as a snack, Parmesan can enhance the flavor of meals without increasing carbohydrate intake, making it a versatile and nutritious option for those following low-carb eating plans.
7. Phosphorus for Energy and Bone Health
Research-Based Insight: Along with calcium, Parmesan cheese is a rich source of phosphorus, a mineral that works closely with calcium to build strong bones and teeth.
Phosphorus also plays a role in energy production by helping the body use carbohydrates and fats. According to the Linus Pauling Institute, phosphorus is also vital for the body’s repair processes, including the maintenance of cells and tissues.
Phosphorus is essential for overall skeletal health and helps maintain the structural integrity of bones. Parmesan’s high phosphorus content ensures that your body has the nutrients needed for both energy metabolism and bone health.
8. Potassium for Blood Pressure Regulation
Research-Based Insight: Although not as potassium-rich as some other foods, Parmesan cheese contains enough potassium to support blood pressure regulation.
Potassium is crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure because it helps balance the effects of sodium in the body, promoting proper blood vessel function.
A study published by the American Heart Association highlighted that potassium-rich diets can help reduce the risk of high blood pressure, especially when consumed alongside calcium and magnesium.
While Parmesan does contain sodium, its potassium content helps counterbalance this, making it a heart-friendly option when enjoyed in moderation.
9. Promotes Satiety and Supports Weight Management
Research-Based Insight: Due to its rich fat and protein content, Parmesan cheese is highly satiating, meaning it helps you feel fuller for longer periods.

A study in the Journal of Obesity revealed that protein- and fat-rich foods like Parmesan can reduce the urge to snack between meals, making it easier to manage calorie intake and maintain a healthy weight.
Parmesan’s strong flavor also means that you can use smaller portions to enhance the taste of your meals without overindulging.
This can help support weight management goals while still allowing you to enjoy a nutrient-dense, satisfying cheese.
10. Cardiovascular Health in Moderation
Research-Based Insight: Despite its fat content, moderate consumption of Parmesan cheese can contribute positively to cardiovascular health.
According to a study in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, the calcium, potassium, and probiotics found in Parmesan cheese can help maintain healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
The probiotics in Parmesan also contribute to better heart health by reducing inflammation, which is linked to cardiovascular diseases.
While it’s important to consume Parmesan in moderation due to its saturated fat content, pairing it with a balanced diet can offer benefits to heart health.
11. Comparing Parmesan to Other Cheeses: Nutritional Superiority
When compared to other common cheeses like cheddar, mozzarella, and feta, Parmesan stands out for its higher concentration of protein and calcium.
While mozzarella is lower in calories and fat, Parmesan contains significantly more calcium and protein per ounce, making it a more nutrient-dense option for those looking to boost their intake of essential nutrients.
Cheddar, another popular cheese, is higher in fat and sodium compared to Parmesan, which makes Parmesan a better choice for those concerned about heart health or weight management.
Parmesan also offers better digestibility due to its lower lactose content compared to other soft cheeses like brie or cream cheese.
12. Parmesan in Various Diets
Parmesan cheese fits well into several dietary patterns, including:
- Mediterranean Diet: Parmesan is often used in moderation in Mediterranean cuisine, paired with vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Paleo Diet: While dairy is limited in strict Paleo diets, some individuals who follow a more lenient version include aged cheeses like Parmesan due to their nutritional density and low lactose content.
- Vegetarian Diet: Parmesan is a great source of protein for vegetarians. However, it’s important to note that traditional Parmesan is made with animal rennet, so vegetarians may need to seek rennet-free varieties.
13. Parmesan Cheese Production: Aging and Nutritional Value
The aging process of Parmesan cheese contributes to its unique flavor and health benefits. Parmesan is aged for a minimum of 12 months, and some varieties are aged for up to 36 months.
During this time, the proteins in the cheese break down into smaller peptides, making it easier to digest and enhancing its probiotic content.

The long aging process also reduces lactose levels and increases the concentration of essential nutrients like calcium and phosphorus, making Parmesan more nutrient-dense comparedto its nutritional density.
The aging process intensifies the cheese’s flavors and nutrient concentration, resulting in higher levels of calcium, phosphorus, and probiotics. This makes Parmesan not only a flavorful addition to your meals but also a nutritional powerhouse.
14. Recipes Featuring Parmesan for Health Benefits
Incorporating Parmesan cheese into your diet can be both nutritious and delicious.
Here are a few healthy ways to use Parmesan in everyday meals:
- Roasted Vegetables with Parmesan: Sprinkle freshly grated Parmesan over roasted vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, or Brussels sprouts for a nutrient boost and added flavor.
- Parmesan-Crusted Chicken: Coat chicken breasts with a mix of grated Parmesan and breadcrumbs for a protein-packed, flavorful meal.
- Parmesan Zucchini Noodles: Swap out regular pasta for zucchini noodles topped with Parmesan and olive oil for a low-carb, nutrient-rich dish.
Parmesan Cheese as a Nutritional Powerhouse
Parmesan cheese is far more than just a delicious topping; it is packed with essential nutrients that benefit overall health.
From its high calcium and protein content to its digestive benefits through probiotics, Parmesan cheese offers numerous health advantages.
When consumed in moderation, Parmesan can support bone health, improve digestion, help manage weight, and even contribute to cardiovascular health.
Incorporating this nutrient-dense cheese into your diet is a great way to enjoy its health benefits while adding rich flavor to your meals.
However, as with any high-fat food, portion control is key to enjoying Parmesan’s benefits without overindulging.
You may like
Health
Level up casino reviews Australia edition
Published
7 months agoon
July 22, 2025By
Wilson MarkLevel up casino reviews Australia edition
In this blunt review, we break down everything you should know about level up casino reviews for Australian players. Find out what matters, which platforms to consider, and pitfalls to avoid. If you’re thinking about joining or comparing online casinos, this is your guide. Get facts, not hype.
Popular Australian Casinos at a Glance
Pokies Madness: Grab 250% Up to $400 & 100 FS
Casino in Your Pocket: 110% Up to $100 & 120 Spins
Pokies Paradise: 200% Up to $2,000 + 150 Free Spins
Start Winning: 300% Bonus Up to $1000 & 75 Spins
Pay with PayID: 50% Match to $400 & 200 Free Spins
Go Big: 175% Welcome Up to $150 & 75 Spins
30% Cashback Every Week – Up to $100 Back
Jump In: 120% Bonus Up to $250 & 40 Free Spins
Aussie Players Welcome: 50% Up to $250 + 60 FS
Welcome Gift: 150% Match Up to $400 + 200 FS Included
Free Play: $100 Bonus + 15 Spins Without a Deposit
Get Started: 300% Bonus Up to $2500 + 150 Free Rounds
Intro Offer: 80% Bonus Up to $400 & 60 Free Spins
Stack the Deck: 300% Match Up to $100 & 75 Spins
Welcome Gift: 150% Match Up to $400 + 200 FS Included
Unlock 20 Free Spins on Your First Deposit
Blackjack Bonus: 80% Up to $750 on Your First Deposit
VIP Lounge Access: 175% Up to $1000 + 100 FS
Midweek Reload: 30% Bonus Up to $300 & 250 FS
High Roller Special: 175% to $3000 + 25 Free Spins
Best slot games on level up casino reviews
Online pokies and slots offer fast, exciting gameplay with instant outcomes and the possibility of sizable rewards. Below, you’ll find a curated selection of the hottest online pokies and slots trending among Australian players. Try your luck or explore new titles directly from home.
Top Online Casino Services and Games
Licensed Australian casinos deliver diverse services, from real money pokies and live-dealer games to poker tables, blackjack, and original skill-based experiences. Level up casino reviews cover which providers offer the best mix. Choose based on your preferences for big wins, variety, or strategy.
Popular Australian Casinos at a Glance
- LevelUp Casino
- Punt Casino
- National Casino
- Casino Rocket
- Fair Go Casino
- Joo Casino
- King Johnnie Casino
Top Online Casino Services and Games
- Online poker rooms
- Real money pokies
- Progressive jackpots
- Live dealer tables
- Blackjack tournaments
- Roulette games
- Baccarat and more
Best Slots and Pokies You Can Play
- Wolf Gold
- Big Bass Bonanza
- Buffalo King
- Gates of Olympus
- Starburst
- Temple Tumble
- Sweet Bonanza
- Book of Dead
- Money Train 2
- Aztec Magic
How Deposits and Withdrawals Work
Australian casino sites make depositing simple with debit cards, e-wallets, and crypto options. Withdrawals usually take from several hours up to five days, with verification needed for first-time requests. Daily and weekly withdrawal limits apply. Review each casino’s financial terms before signing up.
| Payment Method | Deposit Time | Withdrawal Speed |
|---|---|---|
| Visa/MasterCard | Instant | 1-3 days |
| Neosurf | Instant | N/A |
| Bitcoin | Instant | Within 1 day |
| Skrill | Instant | 1-2 days |
Mobile Casino Experience in Australia
Most Aussie online casinos offer sleek mobile sites or dedicated apps for Android and iOS. Features include mobile-only bonuses, quick game loading, and fast deposits. All major pokies and live games work on smartphones and tablets.
Bonuses and Promotions
Welcome packages, no deposit spins, and reload bonuses boost your bankroll. Wagering requirements typically range from 20x to 50x. Always check bonus expiry and eligible games. VIP rewards systems offer cashback, fast payouts, and event tickets for regulars.
Security and Fair Play Ensured
Look for gambling operators licensed by international authorities. All games should use RNG technology for fairness. SSL encryption protects your data. Independent audits are a positive sign. Customer funds should stay segregated from operations accounts.
Customer Support and Player Care
Quality live chat is now standard. Hotlines and email support offer extra layers. Expect a response within minutes during Aussie business hours and detailed FAQ sections for self-help. Multilingual staff are available at leading casino brands.
Responsible Gambling Tools & Advice
Responsible gaming tools include personal deposit caps, self-exclusion, and time trackers. Accredited sites promote responsible gambling organisations. Early signs of unsafe behaviour trigger notifications or account limitations. Seek help if you feel your play is out of control.
Reading the Fine Print: Terms & Conditions
Always read the small print regarding playthroughs, max withdrawal limits, and restricted games. Terms may be updated frequently. Some casinos restrict bonus play for certain games or regions. Careful reading avoids misunderstandings and disappointment.
FAQ – level up casino reviews in Australia
What is level up casino reviews?
Level up casino reviews are independent opinions, overviews, and ratings of major online casinos available in Australia, focusing on features, reliability and user experience.
Are online casinos safe for Australians?
Licensed online casinos use security protocols and fair play policies, but always check for proper regulation before playing.
Can I win real money at Australian online casinos?
Yes, you can win and withdraw real AUD winnings if you play at certified Australian-friendly sites.
Which payment methods can I use?
Common methods include Visa, MasterCard, Neosurf, cryptocurrency, bank transfer, and popular e-wallets.
What are typical bonus wagering requirements?
Most sites ask for wagering your deposit and bonus 20-50 times before withdrawal.
Is there a best time to play online pokies?
No specific time guarantees better odds, as pokies use random number generation for each spin.
Best Online Casinos in Australia 2024
Australia’s iGaming landscape is thriving with fresh brands, innovative games and player-first bonuses, making it a great time to explore top casino sites. Whether you’re into pokies, live tables or sports betting action, the following brands are popular choices among Aussie punters. Get to know which ones stand out and why.
Aussie Play Casino Experience
Aussie Play is well known for its laid-back style and huge pokies library. Players in Australia can expect a very generous welcome bonus, easy registration and local-friendly banking options. Their mobile site works fluently on even basic phones. Customer service is on hand 24/7 via live chat.
Bizzo Casino in the Australian Market
Bizzo has quickly become a favourite due to its fast payments and over 3,000 pokies from top software providers. Aussie players can use AUD for deposits and withdrawals, and weekly free spins offers help keep the excitement high. Their tournaments are a must-try for slot fans.
Caesars Casino Down Under
Caesars, an international casino giant, also accepts Australian players with a sophisticated selection of games. From classic table games to immersive live dealer experiences, it brings a slice of Las Vegas straight to your home. Advanced encryption ensures safe and private gameplay.
Casino Swish for Pokies Fans
Casino Swish makes a mark with its slick interface and huge selection of Aussie-themed pokies. Players can join loyalty programs and claim reload bonuses tailored to regular players. Its payment process is streamlined for local convenience and quick payouts.
Casinonic: Trusted Option for Australians
Australians frequently recommend Casinonic for its speedy withdrawals, secure transactions, and quality games from Pragmatic Play, Microgaming and more. Promotions are frequent and the supporting team is responsive, ensuring an easy experience for new players.
Gets Bet: Sports Betting and More
Gets Bet wraps casino, live casino and sports betting in a single platform, ideal for Aussies who like to combine pokies and wagering. Real-time odds and a seamless mobile app attract sports enthusiasts across the country.
Golden Tiger Casino’s Reputation
Golden Tiger stands out with its big progressive jackpots, frequent bonuses and a reliable Aussie support team. Its desktop and mobile sites both run smoothly, making it a long-standing favourite for Australian casino fans.
High Roller Action
If you like higher stakes, High Roller is tailored for VIP play. Its lavish perks, cashbacks and high deposit limits attract serious punters. Withdrawal times are among the fastest in the segment.
Other Noteworthy Australian Casino Sites
The following brands also have a loyal following in Australia:
- Interwetten brings strong betting options and casino games with fast pay-outs.
- Merkur features top pokies and unique branded games with easy navigation.
- Planet7Casino is famous for on-the-spot cash bonuses and round-the-clock assistance.
-
Poker Star delivers robust poker tournaments and interactive table experiences.
- Royal Ace offers both pokies and table games; attractive for both casual and experienced players.
- SlotJoint gives hundreds of pokies and flexible payment solutions for locals.
- SlottyWay is popular for its exciting slot tournaments and weekly reload bonuses.
- Sportingbet merges betting with casino action, supporting a great range of Aussie sports and slots.
- ThePokies features a local-first approach with loads of Australiana slots.
Uptown Aces and WildCardCity
Uptown Aces focuses on generous welcome bonuses, secure payment options and unique slot themes. WildCardCity is all about urban glamour with VIP privilege schemes and handy support, ensuring top rates of player satisfaction.
WynnBet
WynnBet is gaining pace with mobile-first design and exciting promotions. Its tailored sports and casino offers appeal to players who demand both action and safety.
Responsible Gambling for Australians
Before you start spinning reels or placing wagers, remember to play responsibly. Australia has support services such as Gambling Help Online and phone helplines to provide confidential advice and help you keep gaming fun and safe. Play only with money you can afford and set limits for your entertainment.
Reference only. 18+ / 21+ where applicable
level up casino reviews
Health
Why Do People on Obesity Medications Drink Less Alcohol? Here’s What We Know
Published
1 year agoon
December 14, 2024By
Wilson Mark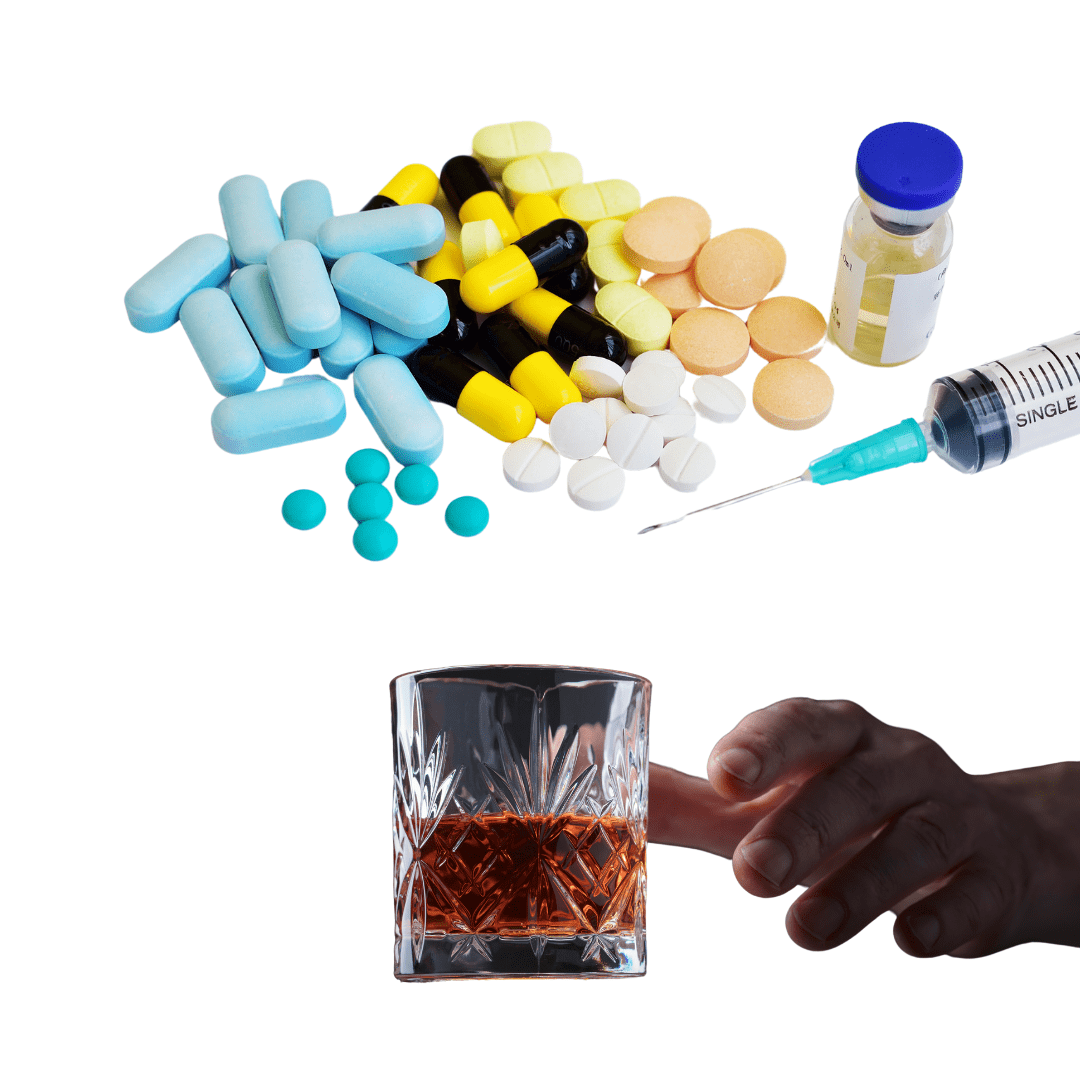
Some people who take anti-obesity medications drink less alcohol. Scientists are trying to figure out why this happens.
How Anti-Obesity Drugs Impact Alcohol Use
Anti-obesity medications, such as Wegovy and Ozempic, may lower alcohol consumption. These drugs, called GLP-1 receptor agonists, are usually prescribed to help with weight loss and type 2 diabetes. However, new research shows they might also reduce drinking habits.
A recent study found that 45% of people on these drugs drank less alcohol. The study, published in JAMA Network Open, involved over 14,000 participants. Researchers believe this connection could lead to more discoveries about these medications.
Key Findings
Here’s what the study revealed:
- Participants: Over 14,000 individuals taking anti-obesity medications.
- Results: 45% of drinkers reduced their alcohol intake.
- Drugs Used: Medications included semaglutide, tirzepatide, and liraglutide.
- Who Benefited Most: Heavy drinkers and people with severe obesity saw the biggest change.
While most participants saw no change, only 2% drank more alcohol.
Why Do These Drugs Affect Alcohol?
The exact reason remains unclear.

However, experts have a few ideas:
- Impact on the Brain: These drugs may reduce cravings by changing how the brain processes rewards. This could lower the desire for alcohol.
- Lifestyle Changes: Many people make healthier choices while on these medications, such as eating better or drinking less.
- Lower Tolerance: Weight loss reduces alcohol tolerance, which might lead people to drink less.
More research is needed to confirm these theories.
Can These Drugs Treat Addiction?
Some experts are hopeful these drugs could help with addiction in the future. However, they are not currently approved for this use.
Dr. Timothy Brennan from Mount Sinai said, “These findings are exciting, but we need more studies to understand their effects on alcohol use.”
Researchers believe these drugs have potential, but it’s too early to draw conclusions.
Should You Avoid Alcohol While Taking These Medications?
You don’t have to stop drinking completely, but experts suggest being cautious.
Here’s why:
- Side Effects: Alcohol may worsen nausea or low blood sugar, which are common side effects of these drugs.
- Calories: Alcohol contains a lot of calories, which could slow your weight-loss progress.
- Health Benefits: Reducing alcohol may improve overall health and make the medication more effective.
If you’re starting a new medication, it’s a good time to evaluate your drinking habits.
What Should You Do?
If you’re prescribed medications like Wegovy or Ozempic, consider these tips:
- Notice if your cravings for alcohol change.
- Take this chance to build healthier habits.
- Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about drinking or other side effects.
What’s Next?
The link between anti-obesity medications and reduced drinking is fascinating. Scientists need more studies to understand how these drugs work.
For now, they remain a powerful option for weight management. The added benefit of possibly reducing alcohol consumption is an exciting bonus.
Health
How to Get Rid of Sulfur Burps: Effective Remedies and Prevention Tips
Published
1 year agoon
November 5, 2024By
Wilson Mark
Sulfur burps may be alleviated by changes in diet, proper water intake, and the use of pharmacy drugs, but it is crucial to know what causes them.
Sulfur Burps
Sulfur burps are bad-odour burps that smell like rotten eggs; many people experience this.
They can be painful and awkward and are sometimes coupled with other abdominal symptoms, including bloating, stomach-churning, or diarrhoea. The foul smell associated with sulfur burps emanates from hydrogen sulfide (H2S) generated inside your stomach.
To know how to treat and get rid of sulfur burps, it is essential to understand the causes that contribute to it.
This article will look at possible causes of sulfur burps, options for natural cure remedies, medical treatment, and ways of avoiding them.
What Causes Sulfur Burps?
Sulfur burps occur when hydrogen sulfide gas builds up in the stomach and is released through burping.

Various factors can contribute to the production of this gas, but here are the most common causes:
- Dietary Choices
Certain foods high in sulfur content can contribute to the production of sulfur gas. Some of these foods include:- Eggs
- Meat (especially red meat)
- Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, and cauliflower
- Garlic and onions
- Dairy products
- Beans and legumes
- Gastrointestinal Infections
Some infections, particularly those caused by bacteria like Helicobacter pylori or parasites like Giardia, can lead to sulfur burps. These infections can disrupt your digestive system, leading to excess gas production. - Indigestion or GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
Indigestion or GERD can slow digestion, allowing food to sit in the stomach longer and produce more gas. This gas can sometimes have a sulfurous smell, leading to sulfur burps. - Food Intolerances
Lactose intolerance, gluten sensitivity, or other food intolerances can cause incomplete digestion of food, leading to gas buildup and sulfur burps. - Medications
Some medications, particularly those containing sulfur compounds or antibiotics that affect the balance of gut bacteria, can contribute to sulfur burps.
Natural Remedies to Get Rid of Sulfur Burps
Although passing sulfur burps might be embarrassing, in most cases, they can be cured naturally. Below, I give you some home remedies that may help if you decide to try:
1. Stay Hydrated

Proper digestion requires that one drink enough water, which is determined by the intensity of the exercises. Drinking fluids eliminates accumulated toxins, thus ensuring the digestive system is working properly, and there is less likelihood of developing gas. Avoid sulfur burps by taking at least eight glasses of water per day.
2. Green Tea or Herbal Teas

Green tea, mint, or chamomile will also relax your tummy and reduce gas formation. Green tea, in particular, has antioxidants that can help with digestion, while peppermint helps to relax the gut.
3. Eat Smaller, More Frequent Meals

Eating large meals or taking more than necessary also puts pressure on the digestive system, resulting in information of gases, including sulfur. Dividing the portions into smaller meals that are taken frequently ensures that the body can break down the food into Sulphur without experiencing sulfur burps.
4. Avoid Sulfur-Rich Foods
If you experience sulfur burps often, you should reduce the intake of sulfur-containing foods such as eggs, broccoli, garlic, and dairy products. These foods may cause more gas production; therefore, cutting down or eliminating these foods from the diet may greatly help.
5. Try Apple Cider Vinegar

Apple cider vinegar (ACV) is one of the go-to home remedies for enhancing digestion. ACV has an impact on balancing the level of acidity in the stomach, hence facilitating the digestion of foods and decreasing the formation of sulfur gas. Ingest a glass of water mixed with 1 tablespoon of ACV, and see if it is taken before meals.
6. Use Probiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that promote healthy digestion by balancing the gut’s bacterial environment. Taking a probiotic supplement or eating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, or sauerkraut can help prevent sulfur burps by keeping your digestive system balanced.
Over-the-Counter Remedies for Sulfur Burps
Several over-the-counter treatments are available if natural remedies aren’t enough to resolve your sulfur burps.
1. Antacids

Many recipes warn about foods that produce gas, but antacids can help neutralize stomach acid and leave your digestive system to do the work. This may be useful, especially if the sulfur burps originate from indigestion or GERD.
Table: Best OTC Medications for Sulfur Burps
| Medication Type | How It Helps | Example Products |
|---|---|---|
| Antacids | Neutralize stomach acid | Tums, Rolaids |
| Simethicone | Breaks up gas bubbles in the stomach | Gas-X, Mylanta Gas |
| Probiotics | Supports gut health | Culturelle, Align, Florastor |
2. Simethicone
It is an anti-gas drug that alters the sizes and distribution of gas in the stomach and intestines, promoting gas release without the smell.
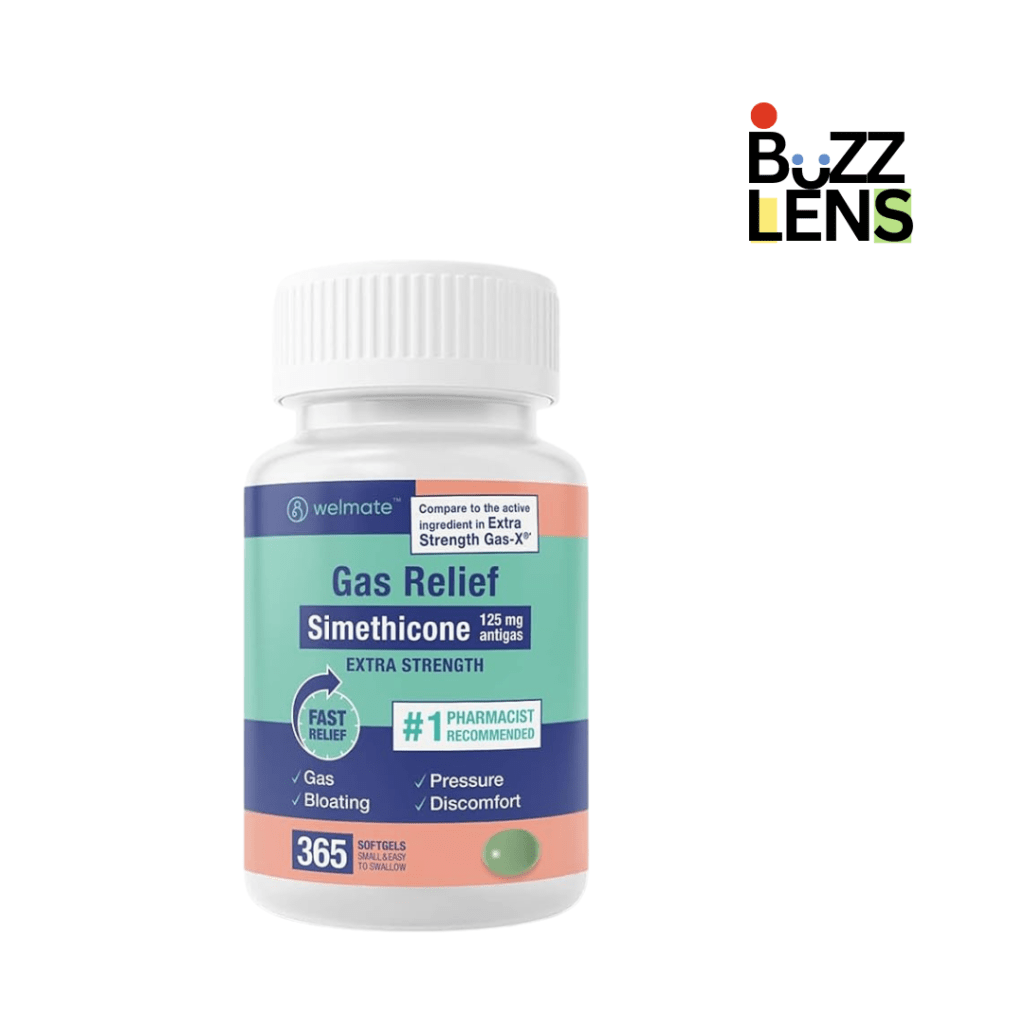
Simethicone-containing products such as Gas-X or Mylanta Gas quickly relieve such pain.
3. Activated Charcoal
Charcoal is effective in absorbing gases and toxins in your stomach. The common formulation is a pill that can successfully minimize normal gas and sulfur-related burps.
Always check with your doctor before using charcoal supplements, as they may interfere with medications.
When to See a Doctor for Sulfur Burps
While sulfur burps are often harmless, they can sometimes signal an underlying health issue that requires medical attention.
If your sulfur burps are persistent or accompanied by other symptoms, such as severe abdominal pain, diarrhoea, nausea, or vomiting, it’s time to consult a doctor.
Here are a few conditions that may require medical evaluation:
1. Gastrointestinal Infections
As mentioned earlier, infections like H. pylori or Giardia can cause sulfur burps and other symptoms like bloating, nausea, diarrhoea, and stomach cramps. Testing for these conditions often involves stool, blood, or breath tests.
2. GERD or Chronic Indigestion
GERD or chronic indigestion can lead to frequent sulfur burps due to slowed digestion. If you experience heartburn, regurgitation, or pain after eating, consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
3. Food Intolerances or Sensitivities
Food intolerances, such as lactose intolerance or celiac disease, may cause sulfur burps. Your doctor may recommend elimination diets or tests to identify specific food triggers.
Prevention Tips: How to Stop Sulfur Burps from Coming Back
Once you’ve gotten rid of sulfur burps, preventing them from returning is essential. Here are some long-term strategies you can follow:
1. Monitor Your Diet
Pay attention to how certain foods affect your digestive system. Keeping a food diary can help you identify which foods trigger your sulfur burps so that you can adjust your diet accordingly.
2. Eat Slowly and Chew Thoroughly
Eating too quickly can cause you to swallow air, leading to gas and burping. Chewing food thoroughly helps your digestive system break down food more efficiently, reducing the chance of sulfur gas forming.
3. Avoid Carbonated Beverages
Carbonated drinks like soda and sparkling water introduce extra air into your stomach, which can lead to burping. Try to cut down on these beverages to reduce gas and sulfur burps.
4. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity can improve digestion by keeping things moving through your gastrointestinal tract. Even light activities like walking after a meal can help prevent gas buildup.
5. Stay Hydrated
Hydration is vital to maintaining healthy digestion. Water helps break down food and keeps things moving through your digestive system, reducing the likelihood of gas formation.
Banish Sulfur Burps for Good
Sulfur burps may be unpleasant, but they’re usually treatable with dietary changes, natural remedies, and over-the-counter medications.
Whether you’re dealing with a one-time issue or chronic sulfur burps, identifying the underlying cause is the first step toward relief.
By adjusting your diet, staying hydrated, and trying some of the remedies outlined here, you can eliminate sulfur burps and prevent them from returning.
Remember, if sulfur burps persist or are accompanied by other severe symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider to rule out any underlying health issues.


iOS 26 Explained: Stability & The Future of iPhones
Level up casino reviews Australia edition
Magnitude 5.1 Earthquake Rattles Northern Iran — No Major Damage Reported
Trending
-

 FASHION9 years ago
FASHION9 years agoThese ’90s fashion trends are making a comeback in 2017
-

 Entertainment9 years ago
Entertainment9 years agoThe final 6 ‘Game of Thrones’ episodes might feel like a full season
-

 FASHION9 years ago
FASHION9 years agoAccording to Dior Couture, this taboo fashion accessory is back
-

 Entertainment9 years ago
Entertainment9 years agoDisney’s live-action Aladdin finally finds its stars
-

 Sports9 years ago
Sports9 years agoBoxing continues to knock itself out with bewildering, incorrect decisions
-

 Entertainment9 years ago
Entertainment9 years agoThe old and New Edition cast comes together to perform
-

 Sports9 years ago
Sports9 years agoPhillies’ Aaron Altherr makes mind-boggling barehanded play
-

 Sports9 years ago
Sports9 years agoSteph Curry finally got the contract he deserves from the Warriors




