FITNESS
Why Steady-State Cardiovascular Exercise Is Key to Long-Term Fitness
Discover the benefits of steady-state cardiovascular exercise, including improved heart health, increased endurance, and stress reduction. Learn how to incorporate steady-state cardio into your fitness routine for long-term health.
Published
2 years agoon
By
Admin
Steady-state cardiovascular exercise, often simply referred to as “steady-state cardio,” is a popular and effective way to improve cardiovascular health, increase endurance, and burn calories.
Unlike high-intensity interval training (HIIT), which involves short bursts of intense activity followed by rest, steady-state cardio is characterized by maintaining a consistent level of intensity over an extended period.
This form of exercise has been a staple in fitness routines for decades, and for good reason.
In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of steady-state cardiovascular exercise and how you can incorporate it into your fitness regimen.
What is Steady-State Cardiovascular Exercise?

Steady-state cardio involves performing an aerobic activity, such as running, cycling, swimming, or walking, at a consistent intensity for a prolonged period, usually 30 minutes or more.
The goal is to maintain a steady heart rate, typically within 55-75% of your maximum heart rate, which can be calculated as 220 minus your age.
This moderate-intensity exercise helps to improve cardiovascular endurance and overall fitness.
Related Article: Your Ultimate Guide to Planet Fitness: Affordable Fitness for Everyone
Benefits of Steady-State Cardiovascular Exercise
- Improved Cardiovascular Health
One of the primary benefits of steady-state cardio is its positive impact on cardiovascular health. Regular participation in steady-state exercise can strengthen the heart muscle, improve blood circulation, and lower blood pressure. This reduces the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Increased Endurance
Steady-state cardio is excellent for building endurance. By engaging in prolonged aerobic activity, your body becomes more efficient at using oxygen, which enhances your stamina and allows you to perform physical activities for longer periods without fatigue.
- Effective Calorie Burning
While steady-state cardio may not burn calories as quickly as HIIT, it is still an effective way to burn calories and lose weight. The sustained effort over a longer duration can lead to significant calorie expenditure, making it a valuable tool for weight management.
- Stress Reduction
Exercise, in general, is known for its stress-relieving benefits, and steady-state cardio is no exception. The rhythmic and repetitive nature of activities like running or cycling can help clear your mind, reduce stress levels, and promote mental well-being.
- Low Risk of Injury
Compared to high-intensity workouts, steady-state cardio is generally easier on the joints and muscles, making it a safer option for individuals with injuries or those new to exercise. It allows you to build fitness gradually without the risk of overtraining or injury.
- Improved Mental Health
Regular steady-state exercise has been shown to boost mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression. The release of endorphins during exercise helps to create a sense of well-being and positivity, making it an excellent activity for maintaining mental health.
How to Incorporate Steady-State Cardio into Your Routine
- Choose an Activity You Enjoy
The key to maintaining a consistent exercise routine is finding an activity you enjoy. Whether it’s running, swimming, cycling, or walking, choose something that you look forward to doing.
- Start Slow and Gradually Increase Intensity
If you’re new to steady-state cardio, start with shorter sessions and gradually increase the duration and intensity as your fitness improves. Aim for 30-60 minutes of steady-state cardio 3-5 times a week.
- Mix it Up
To prevent boredom and overuse injuries, vary your cardio activities. Alternate between different exercises, such as running one day and cycling the next. This not only keeps your routine interesting but also challenges different muscle groups.
- Monitor Your Heart Rate
To ensure you’re working within your target heart rate zone, consider using a heart rate monitor. This helps you maintain the appropriate intensity level and maximize the benefits of your workout.
- Listen to Your Body
While steady-state cardio is generally safe, it’s important to listen to your body. If you experience pain or discomfort, adjust the intensity or duration of your workout. Rest and recovery are essential components of any fitness routine.
The Long-Term Benefits of Steady-State Cardio
Steady-state cardiovascular exercise is a valuable addition to any fitness routine, offering a wide range of physical and mental health benefits.
By incorporating steady-state cardio into your weekly regimen, you can improve your cardiovascular health, increase endurance, manage your weight, and reduce stress.
Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or a fitness novice, steady-state cardio is a sustainable and effective way to achieve long-term health and wellness.
You may like
FITNESS
A Faster Way to Fat Loss: Effective Strategies for Sustainable Weight Loss
Published
1 year agoon
September 30, 2024By
Wilson Mark
The faster way to fat loss includes a combination of intermittent fasting, strategic exercise, and a balanced diet with a focus on whole foods, all of which help promote efficient fat burning and long-term results.
The Importance of Fat Loss
Many people aim to lose fat not only to enhance their appearance but also to improve overall health. Excess body fat is linked to numerous health conditions, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and high blood pressure.
For those seeking quick yet effective methods for fat loss, adopting the right strategies is crucial to achieving sustainable results without compromising health.
This article outlines several scientifically-backed methods that accelerate the fat loss process, focusing on intermittent fasting, exercise, diet adjustments, and lifestyle changes.
Intermittent Fasting: A Simple, Effective Approach
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a method of eating that cycles between periods of fasting and eating. It’s not about restricting what you eat but rather when you eat.

Popular IF methods include:
- 16/8 method: Fast for 16 hours and eat during an 8-hour window.
- 5:2 method: Eat normally for five days, and consume only 500-600 calories on two non-consecutive days.
How Does Intermittent Fasting Aid Fat Loss?
When you fast, insulin levels drop, which encourages the body to use stored fat for energy. Additionally, fasting promotes the release of norepinephrine, a hormone that helps break down body fat. Studies show that intermittent fasting can lead to 3-8% fat loss over 3-24 weeks.
Also Read: Intermittent Fasting: Discover the Latest Health Benefits
Exercise: Combining Strength and Cardio for Optimal Results
Strength Training
Strength training is one of the most effective ways to accelerate fat loss. Unlike cardio, which primarily burns calories during the exercise, strength training increases your resting metabolic rate (RMR). This means that your body continues to burn calories even after your workout is over.
Examples of strength training exercises include:
- Weight lifting.
- Bodyweight exercises (e.g., push-ups, squats, lunges).
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods. HIIT is known for its efficiency in burning fat, as it keeps the heart rate elevated and stimulates the metabolism.

Benefits of HIIT include:
- Increased fat burning during and after the workout (known as the afterburn effect).
- Improved cardiovascular health.
- Shorter workout durations (20-30 minutes).
Cardio Workouts
Incorporating cardio is important for burning extra calories. Activities like running, cycling, and swimming help increase the calorie deficit, which is essential for fat loss.
Aim for 150-300 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio per week to maximize fat burning.
Also Read: 9 Unexpected Symptoms Cardiologists Warn You Should Never Overlook
Diet for Faster Fat Loss: Focusing on Whole Foods
Prioritize Protein
Protein is the most important macronutrient for fat loss. Not only does it keep you feeling full for longer, but it also helps preserve muscle mass during weight loss. Maintaining muscle mass is key to keeping the metabolism high.

Great sources of protein include:
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey, fish).
- Eggs.
- Legumes (beans, lentils).
- Greek yogurt.
Limit Refined Carbohydrates and Sugars
To lose fat effectively, it’s important to reduce the intake of refined carbohydrates and added sugars, which cause insulin spikes and promote fat storage. Instead, opt for complex carbs like whole grains, vegetables, and fruits, which provide long-lasting energy and promote satiety.
Incorporate Healthy Fats
While it may seem counterintuitive, eating healthy fats can support fat loss. Foods rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats help maintain hormonal balance and reduce cravings.
Healthy fat sources include:
- Avocados.
- Nuts and seeds.
- Olive oil.
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel).
Also Read: Understanding the Blood Type Diet: How It Works and Its Benefits
Creating a Caloric Deficit: The Key to Fat Loss
In order to lose fat, your body needs to burn more calories than it consumes. This concept is known as a caloric deficit.
Here’s how to achieve it:
- Track your intake: Use a calorie-tracking app to monitor how much you’re eating.
- Calculate your calorie needs: Determine your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) and adjust your intake based on your activity level.
- Reduce calorie intake: Aim for a 500-700 calorie deficit per day to lose around 1-2 pounds of fat per week, which is considered safe and sustainable.
| Caloric Deficit Example | Calories |
|---|---|
| Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) | 2000 |
| Calories Burned Through Exercise | 300 |
| Total Daily Calories Needed | 2300 |
| Target Deficit (for fat loss) | 500 |
| Total Daily Caloric Intake | 1800 |
Lifestyle Habits to Accelerate Fat Loss
Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water throughout the day supports fat loss by:
- Reducing appetite: Sometimes, the body can confuse thirst with hunger.
- Boosting metabolism: Studies have shown that drinking cold water increases metabolic rate as the body works to warm it.
Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water per day.
Get Quality Sleep
Lack of sleep is closely linked to weight gain and fat storage. Sleep deprivation can disrupt hormones like ghrelin and leptin, which regulate hunger and fullness, leading to increased cravings.

Make sure to get 7-9 hours of sleep each night to promote fat loss.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can elevate cortisol levels, which is linked to increased fat storage, especially around the abdomen. Incorporating stress-management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or even short walks can help manage cortisol levels and support fat loss.
Also Read: Relaxing Study Music for Focus: Deep Concentration & Stress-Free Learning
Tracking Your Progress
As you work towards fat loss, it’s essential to track your progress in various ways:
- Weigh yourself: Do this once a week, ideally at the same time of day.
- Take body measurements: Monitor waist, hip, and thigh measurements to track fat loss.
- Check body fat percentage: Some scales can estimate body fat, or you can use tools like calipers.
While the scale is one indicator of progress, remember that losing fat and gaining muscle may cause fluctuations that don’t always reflect your true progress.
Avoid Common Fat Loss Mistakes
Drastic Calorie Cutting
While it’s tempting to cut calories drastically for faster results, doing so can backfire.
Extreme calorie restriction can lead to:
- Muscle loss.
- A slowed metabolism.
- Nutrient deficiencies.
Relying on Quick Fixes
Fad diets or extreme workout plans may promise fast results, but they are often unsustainable. Focus on long-term changes that can be maintained for a healthier, more effective fat loss journey.
Achieving Sustainable Fat Loss
The faster way to fat loss isn’t about extreme dieting or hours of exercise. Instead, it combines intermittent fasting, exercise, and a balanced diet to achieve long-term, sustainable fat loss.
Incorporating healthy lifestyle habits such as staying hydrated, managing stress, and ensuring quality sleep further supports your efforts.
By following these strategies, you can accelerate your fat loss while preserving muscle mass and enhancing your overall health.
Focus on consistency, track your progress, and make adjustments as needed for a successful fat loss journey.
FITNESS
Kettlebell Workout: Full-Body Exercises for Strength and Fat Loss
Published
1 year agoon
September 25, 2024By
Admin
A well-designed kettlebell workout provides a full-body exercise routine, improving strength, endurance, and fat loss through dynamic movements and functional training.
Why Choose Kettlebell Workouts?
Kettlebell workouts have gained immense popularity due to their ability to deliver a comprehensive full-body workout in a short amount of time.

Unlike traditional weights, kettlebells require you to engage your core and stabilizing muscles, making them perfect for functional training.
Whether your goal is to build strength, burn fat, or improve endurance, incorporating kettlebells into your workout routine is an effective way to achieve those fitness goals.
Benefits of Kettlebell Workouts
Kettlebells are versatile and offer numerous benefits, including:
Full-Body Conditioning
Kettlebell exercises engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, providing a full-body workout. Whether you’re doing swings, presses, or cleans, you’re working your arms, shoulders, core, and legs all at once.
Cardiovascular and Strength Training
One of the biggest advantages of kettlebell workouts is that they combine both cardio and strength training. Kettlebell movements like the swing or snatch keep your heart rate elevated, while the resistance of the kettlebell builds muscle.
Also Read: 9 Unexpected Symptoms Cardiologists Warn You Should Never Overlook
Functional Movement
Kettlebell exercises focus on functional movement patterns that mimic everyday actions, improving your overall mobility, stability, and coordination. Movements like the kettlebell clean and Turkish get-up are excellent examples of functional training.
Fat Loss
Because kettlebell workouts engage large muscle groups, they are highly effective for fat burning. The combination of cardio and strength means you’re burning calories during and after your workout, thanks to the afterburn effect.
Also Read: Healthiest Protein Bars: Top Picks for Nutrition, Taste, and Fitness Goals
Time Efficiency
Kettlebell workouts are incredibly time-efficient. A 20–30 minute session can provide the benefits of both a cardio and strength workout, making it ideal for people with busy schedules.
Essential Kettlebell Exercises for a Full-Body Workout
Below are some fundamental kettlebell exercises that target all major muscle groups, providing a balanced full-body workout.
Kettlebell Swing
The kettlebell swing is one of the most effective kettlebell exercises, targeting your glutes, hamstrings, core, and back. It also delivers a cardio boost.

How to do it:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Grip the kettlebell with both hands, hinge at your hips, and swing the kettlebell between your legs.
- Use the power from your hips to swing the kettlebell forward to chest height, keeping your arms straight.
- Repeat for 10–15 reps.
Kettlebell Goblet Squat
This exercise targets the legs, glutes, and core while also improving mobility in the hips.
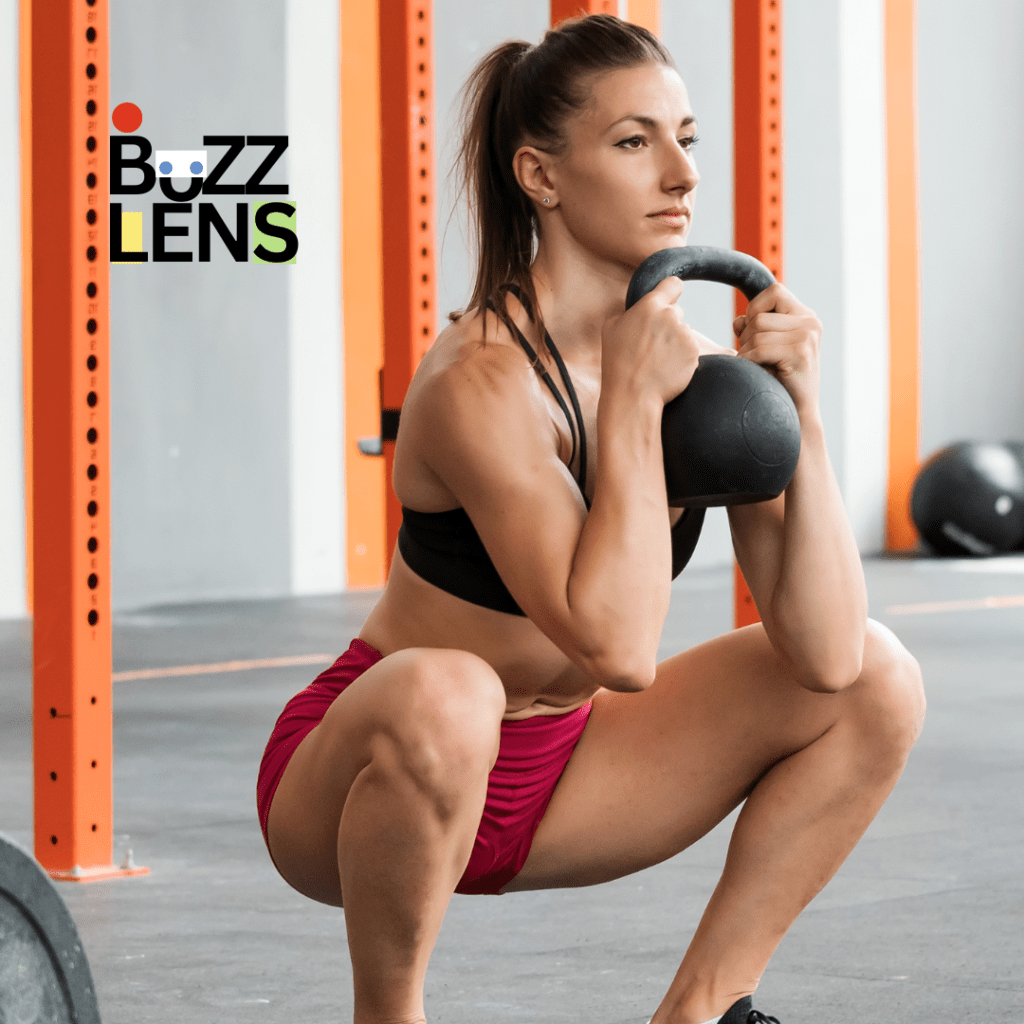

How to do it:
- Hold the kettlebell by the horns at chest height.
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart and squat down, keeping your back straight.
- Lower until your thighs are parallel to the ground.
- Push through your heels to return to the starting position.
- Perform 10–12 reps.
Kettlebell Deadlift
The kettlebell deadlift strengthens your hamstrings, glutes, and lower back while teaching proper hip hinge mechanics.

How to do it:
- Stand with feet hip-width apart and the kettlebell between your feet.
- Bend at your hips and knees, grab the kettlebell handle, and lift it by extending your hips and knees.
- Squeeze your glutes at the top, then lower the kettlebell back to the ground.
- Repeat for 10–12 reps.
Also Read: Why Steady-State Cardiovascular Exercise Is Key to Long-Term Fitness
Kettlebell Clean and Press
This dynamic exercise works your shoulders, arms, core, and legs, providing an excellent combination of power and stability.

How to do it:
- Start with the kettlebell between your feet.
- Clean the kettlebell to your shoulder by pulling it up, rotating your hand as it comes to rest at shoulder height.
- Press the kettlebell overhead, fully extending your arm.
- Lower it back to the ground and repeat on the opposite side.
- Perform 8–10 reps per side.
Turkish Get-Up
A Turkish get-up is a complex movement that engages almost every muscle in the body, especially your core, shoulders, and hips.

How to do it:
- Lie on your back holding a kettlebell in one hand with your arm extended.
- Bend the knee on the same side, and push yourself onto your opposite elbow.
- Transition to a seated position, then to a lunge, and finally stand up.
- Reverse the movement back to the starting position.
- Perform 3–5 reps per side.
Sample Kettlebell Workout Routine
Here’s a sample kettlebell workout that you can follow. Perform the exercises as a circuit, meaning you’ll move from one exercise to the next with minimal rest in between.
| Exercise | Reps | Sets |
|---|---|---|
| Kettlebell Swing | 15 reps | 3 |
| Goblet Squat | 12 reps | 3 |
| Kettlebell Deadlift | 12 reps | 3 |
| Clean and Press (each side) | 10 reps | 3 |
| Turkish Get-Up (each side) | 5 reps | 3 |
| Rest between circuits | 1-2 minutes |
You can modify the number of sets and reps based on your fitness level, adding more as you become stronger.
How to Choose the Right Kettlebell Weight
When starting out, choosing the right kettlebell weight is crucial for proper form and avoiding injury.
Here are some general guidelines:
- Beginners: For women, a weight between 8–12 kg (18–26 lbs) is usually ideal. For men, starting with 12–16 kg (26–35 lbs) is appropriate.
- Intermediate and Advanced Lifters: Once you become familiar with the movements, you can progress to heavier kettlebells, typically ranging from 16–24 kg (35–53 lbs) for women and 24–32 kg (53–70 lbs) for men.
Always prioritize form over weight. It’s better to use a lighter kettlebell with proper technique than a heavier one that causes you to compromise on form.
Safety Tips for Kettlebell Workouts
To ensure you’re getting the most out of your kettlebell workouts without risking injury, follow these safety tips:
- Warm-Up Properly: Always warm up before starting your kettlebell routine. Dynamic movements like arm circles, hip rotations, and leg swings are great to prepare your body.
- Master Form First: If you’re new to kettlebells, start with lighter weights and focus on mastering form before increasing the intensity.
- Engage Your Core: Most kettlebell movements involve a lot of core engagement. Keep your core tight and spine neutral to prevent strain on your lower back.
- Control the Kettlebell: Avoid swinging the kettlebell out of control. All movements should be smooth and controlled, even during fast-paced exercises.
Why Kettlebell Workouts Are a Game-Changer
Kettlebell workouts offer a unique and powerful way to combine strength training, cardio, and functional movement into one efficient routine.
Whether you are looking to build muscle, lose fat, or improve overall fitness, kettlebells provide the versatility needed to meet your goals.
By incorporating a combination of exercises like swings, squats, and presses, you’ll not only enhance strength and endurance but also improve your mobility and coordination.
With consistent practice and proper technique, kettlebell workouts can transform your fitness level in a shorter amount of time than traditional weight training routines.
FITNESS
Healthiest Protein Bars: Top Picks for Nutrition, Taste, and Fitness Goals
Published
1 year agoon
September 22, 2024By
Admin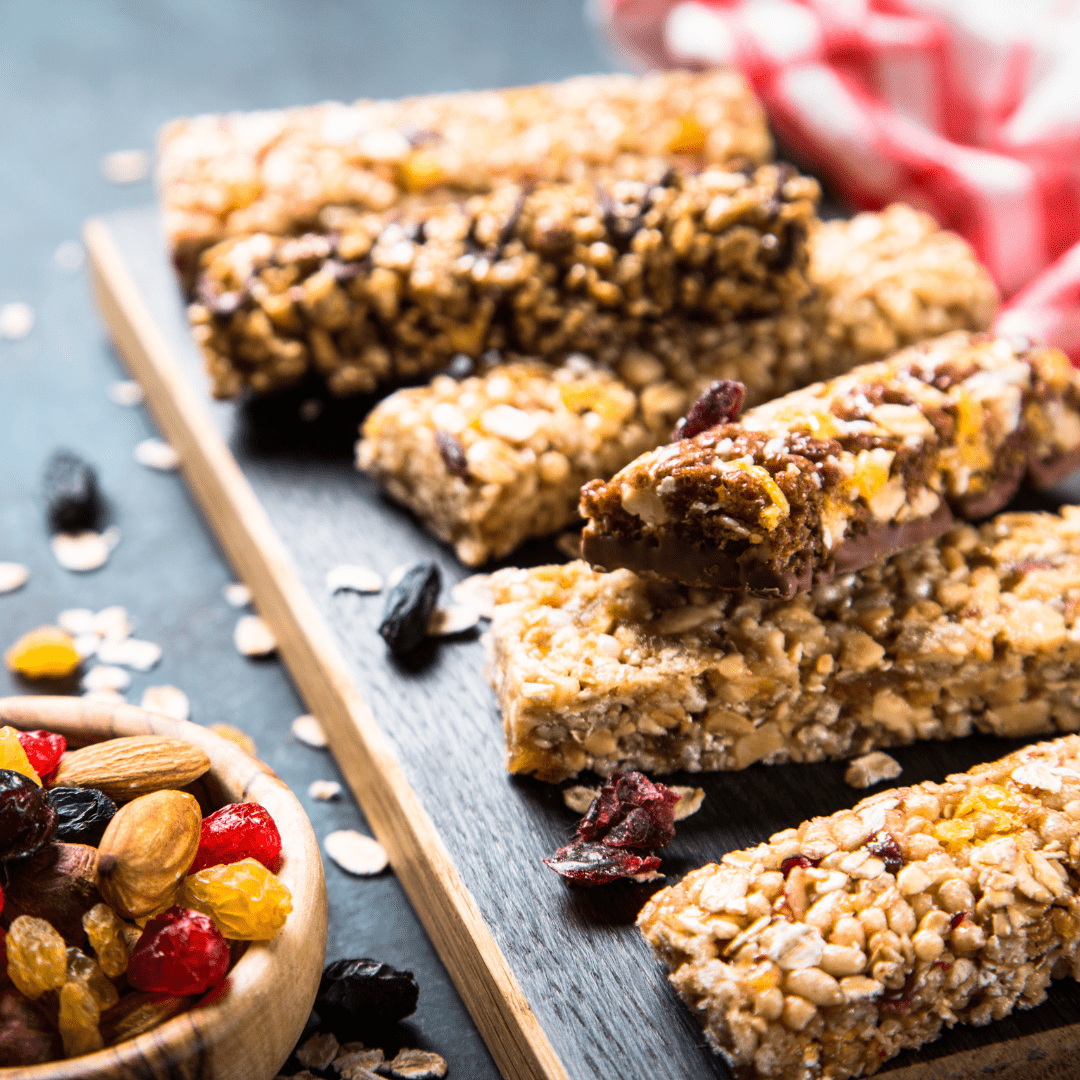
Healthiest Protein Bars: Top choices include RXBAR, Kind Protein Bars, Quest Bars, and GoMacro Bars, each offering balanced nutrition to support muscle recovery, weight management, and long-lasting energy.
Why Choose a Healthy Protein Bar?
Protein bars have surged in popularity, offering a quick and convenient way to boost protein intake.
Whether you’re looking for a post-workout recovery snack, something to curb mid-day hunger, or a portable meal replacement, a well-chosen protein bar can serve as a healthy option.
However, not all protein bars are as nutritious as they appear. Some are loaded with added sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial ingredients, which can negate their potential benefits.
Choosing a healthy protein bar means finding one that provides high-quality protein, fiber, and low sugar content.
The right protein bar can help with muscle recovery, weight management, and sustaining energy levels throughout the day. But which bars are the healthiest?
Let’s explore what to look for and examine the top options available on the market.
What to Look for in a Healthy Protein Bar
Not every protein bar is created equally, and knowing what to look for is key to choosing a product that aligns with your health goals.
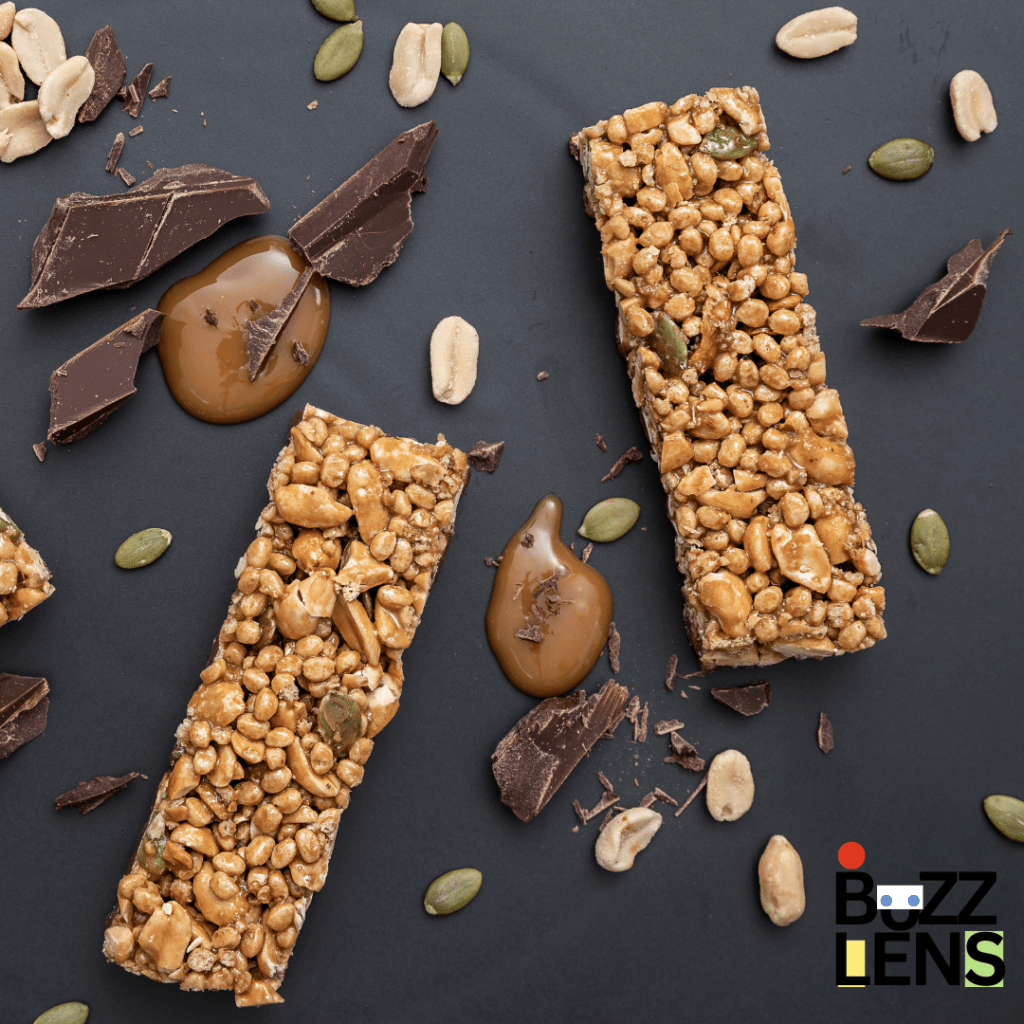

Here are some important factors to consider:
1. Protein Content
The main goal of a protein bar is to increase your daily protein intake, making it essential to look for bars with at least 10-20 grams of protein per serving. For those looking to build muscle or recover from a workout, a higher protein content closer to 20 grams may be optimal.
2. Low Sugar
Many protein bars contain added sugars that can cause blood sugar spikes and weight gain. Ideally, look for bars with less than 5 grams of sugar per serving, and avoid those sweetened with high fructose corn syrup or artificial sweeteners like sucralose.
3. Fiber Content
Fiber plays a crucial role in promoting digestive health and keeping you full longer. Choose protein bars with at least 3-5 grams of fiber per serving to help regulate blood sugar and support digestion.
4. Quality Ingredients
A high-quality protein bar should contain whole foods and minimal artificial additives. Look for bars made with nuts, seeds, whole grains, and protein sources like whey, pea protein, or egg whites. Avoid bars with long lists of preservatives, fillers, and processed ingredients.
5. Calories and Carbohydrates
For those watching their calorie or carbohydrate intake, choose bars that fit within your dietary needs. Bars with less than 200 calories and low net carbs are great for weight management or those on low-carb diets.
Also Read: Why Steady-State Cardiovascular Exercise Is Key to Long-Term Fitness
Top Healthiest Protein Bars
Here are some of the best protein bars on the market, chosen for their nutritional quality, taste, and ingredients:
1. RXBAR

- Protein: 12 grams per bar (from egg whites, nuts, and dates)
- Sugar: No added sugars, sweetened with dates
- Fiber: 5 grams
- Why It’s Great: RXBAR is celebrated for its clean label—containing just a handful of whole ingredients. It’s free from added sugars, preservatives, and artificial sweeteners, making it a solid choice for those who prefer natural, minimally processed foods. Each bar is packed with egg whites for protein, nuts for healthy fats, and dates for natural sweetness.
2. Kind Protein Bars

- Protein: 12 grams per bar (from nuts and soy protein isolate)
- Sugar: 8 grams (from natural sources like honey)
- Fiber: 5 grams
- Why It’s Great: Kind bars are known for using whole food ingredients, primarily nuts and seeds, to create a protein-packed, fiber-rich snack. While they do contain some sugar from honey, their balance of protein, fiber, and healthy fats makes them filling and nutritious.
3. Quest Bars

- Protein: 20 grams per bar (from whey protein isolate and milk protein isolate)
- Sugar: 1 gram
- Fiber: 14 grams
- Why It’s Great: Quest Bars are a favorite among fitness enthusiasts for their high protein content and low sugar. They are sweetened with erythritol and stevia, making them low in carbohydrates while still being sweet. Their 14 grams of fiber help promote digestive health and keep you feeling full longer, making them ideal for post-workout recovery or a quick meal replacement.
Also Read: Your Ultimate Guide to Planet Fitness: Affordable Fitness for Everyone
4. GoMacro Bars

- Protein: 10-12 grams per bar (from pea protein and brown rice protein)
- Sugar: 10-12 grams (from organic sources like coconut sugar and brown rice syrup)
- Fiber: 4 grams
- Why It’s Great: These bars are vegan, organic, and non-GMO, making them a perfect choice for those who prioritize sustainable and plant-based nutrition. Though they contain more natural sugars, their whole food ingredients and plant-based protein make them a great option for vegan and health-conscious consumers.
5. No Cow Protein Bars

- Protein: 21 grams per bar (from pea protein and rice protein)
- Sugar: 1 gram (sweetened with stevia and erythritol)
- Fiber: 16 grams
- Why It’s Great: As the name suggests, No Cow Protein Bars are dairy-free and vegan, using plant-based protein sources. They are high in fiber and protein, making them a solid choice for those following a low-carb or keto diet. With just 1 gram of sugar, they offer an excellent balance of nutrition without the carb load.
6. Clif Builder’s Protein Bars

- Protein: 20 grams per bar (from soy protein isolate)
- Sugar: 17 grams
- Fiber: 3 grams
- Why It’s Great: Though these bars are higher in sugar than others on this list, they are a favorite among athletes due to their high protein content and ability to fuel strenuous workouts. Clif Builder’s Bars are great for those who need extra calories and protein for energy-intensive activities like hiking or cycling.
Also Read: Comprehensive Health Benefits of Hearts of Palm
Comparing Protein Sources: Plant-Based vs. Whey Protein
When it comes to protein bars, the protein source can vary significantly and may affect your digestion, energy levels, and muscle recovery.
Here’s a breakdown of the two most common protein sources:
1. Whey Protein
Whey protein is derived from milk and is one of the most popular protein sources for its complete amino acid profile.

It’s easily absorbed by the body, making it ideal for muscle repair and post-workout recovery.
Bars like Quest Bars and Clif Builder’s Bars utilize whey protein to deliver a high protein content for athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
2. Plant-Based Protein
For those who prefer vegan or dairy-free options, plant-based protein bars use protein sources such as pea protein, rice protein, or hemp protein.

Though plant-based proteins may not be as easily absorbed as whey, they still provide a healthy dose of protein, and when combined with other plant sources, they can offer a complete amino acid profile.
No Cow Bars and GoMacro Bars are excellent examples of bars using plant-based proteins.
Benefits of Choosing Healthy Protein Bars
Incorporating healthy protein bars into your diet offers several benefits:
1. Supports Muscle Recovery
Consuming protein after exercise is essential for repairing muscle fibers and encouraging muscle growth. Protein bars with at least 20 grams of protein, like Quest Bars and Clif Builder’s Bars, are excellent for muscle recovery.
2. Promotes Weight Management
High-protein, low-sugar bars help you stay full longer and avoid the temptation of high-calorie, sugary snacks. Protein bars with fiber and minimal sugar can help manage cravings and provide sustained energy without a sugar crash.
3. Convenient Meal Replacement
For those on the go, protein bars offer a balanced, portable meal replacement. Bars with whole food ingredients and a balance of protein, fiber, and healthy fats, like RXBAR and Kind Protein Bars, are filling and nutritious alternatives to processed snacks.
4. Digestive Health
Bars high in fiber, such as Quest Bars and No Cow Protein Bars, promote digestive regularity and gut health. Fiber is essential for feeding the healthy bacteria in your gut, supporting digestion, and regulating bowel movements.
Also Read: Health Benefits of Parmesan Cheese: A Deep Dive into Nutritional Advantages
Potential Drawbacks of Protein Bars
While protein bars are convenient and healthy options, it’s important to be mindful of some potential drawbacks:
1. Hidden Sugars
Even bars marketed as healthy can contain added sugars that spike blood sugar levels. Always check the ingredient list and nutrition label for hidden sugars, especially those that rely heavily on natural sweeteners like brown rice syrup or agave.
2. Artificial Sweeteners
While many protein bars use artificial sweeteners to reduce sugar content, these can cause digestive discomfort in some people, leading to bloating or gas. Bars that use sweeteners like sucralose, aspartame, or even sugar alcohols like erythritol may cause issues for those with sensitive stomachs.
3. Highly Processed Ingredients
Some protein bars contain a long list of processed ingredients, which can reduce their nutritional value. Instead of opting for overly processed bars with additives, choose those made from whole foods, such as RXBAR or Kind Protein Bars.
Protein Bars for Specific Health Goals
Different protein bars can serve various health goals.
Here’s how to choose the right one based on your specific needs:
1. Weight Loss
If your goal is to lose weight, look for bars that are low in calories, high in protein, and low in sugar. Bars like Quest Bars and No Cow Protein Bars are great options because they contain minimal sugar and offer plenty of fiber to keep you full.
2. Muscle Gain
For those focused on building muscle, bars with higher protein content (20 grams or more) are ideal. Clif Builder’s Bars and Quest Bars are excellent for promoting muscle recovery and growth post-workout.
3. Vegan or Plant-Based Diet
If you follow a plant-based or vegan diet, opt for bars like GoMacro Bars or No Cow Bars, which use plant-based protein sources like pea protein or rice protein. These bars offer a substantial amount of protein while adhering to vegan dietary guidelines.
Comparing Protein Bars: A Quick Overview
| Brand | Protein (grams) | Sugar (grams) | Fiber (grams) | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RXBAR | 12 | 0 (no added sugar) | 5 | Clean, whole ingredients |
| Kind Protein Bars | 12 | 8 | 5 | Nut-based, whole foods |
| Quest Bars | 20 | 1 | 14 | Low carb, high protein |
| GoMacro Bars | 10-12 | 10-12 | 4 | Vegan, organic |
| No Cow Protein Bars | 21 | 1 | 16 | Dairy-free, vegan |
| Clif Builder’s Bars | 20 | 17 | 3 | High calorie, great for athletes |
Choosing the Healthiest Protein Bar for Your Needs
The healthiest protein bars combine high-quality protein, low sugar, and minimal processing, making them a perfect snack or meal replacement.
Whether you’re seeking post-workout recovery, weight management, or simply a healthy snack, options like RXBAR, Kind Protein Bars, Quest Bars, GoMacro Bars, and No Cow Protein Bars provide delicious and nutritious choices.
Always consider your specific health goals when choosing a bar, and opt for products made with whole foods, balanced nutrition, and no added sugars.
By understanding what to look for in a protein bar and selecting from the healthiest options available, you can incorporate this convenient snack into your daily routine while supporting your overall health and fitness goals.


iOS 26 Explained: Stability & The Future of iPhones
Level up casino reviews Australia edition
Magnitude 5.1 Earthquake Rattles Northern Iran — No Major Damage Reported
Trending
-

 FASHION9 years ago
FASHION9 years agoThese ’90s fashion trends are making a comeback in 2017
-

 Entertainment9 years ago
Entertainment9 years agoThe final 6 ‘Game of Thrones’ episodes might feel like a full season
-

 FASHION9 years ago
FASHION9 years agoAccording to Dior Couture, this taboo fashion accessory is back
-

 Entertainment9 years ago
Entertainment9 years agoDisney’s live-action Aladdin finally finds its stars
-

 Sports9 years ago
Sports9 years agoBoxing continues to knock itself out with bewildering, incorrect decisions
-

 Entertainment9 years ago
Entertainment9 years agoThe old and New Edition cast comes together to perform
-

 Sports9 years ago
Sports9 years agoPhillies’ Aaron Altherr makes mind-boggling barehanded play
-

 Sports9 years ago
Sports9 years agoSteph Curry finally got the contract he deserves from the Warriors




